domingo, junho 29, 2008
sábado, junho 28, 2008
As Consequências Mentais do Ateísmo?
Atheism and Mental and Physical Health
- See main article: Atheism and Mental and Physical Health
The is considerable amount of scientific evidence that suggest that theism is more conducive to mental and physical health than atheism.[68][69] The prestigious Mayo Clinic reported the following on December 11, 2001:
| “ | In an article also published in this issue of Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Mayo Clinic researchers reviewed published studies, meta-analyses, systematic reviews and subject reviews that examined the association between religious involvement and spirituality and physical health, mental health, health-related quality of life and other health outcomes.The authors report a majority of the nearly 350 studies of physical health and 850 studies of mental health that have used religious and spiritual variables have found that religious involvement and spirituality are associated with better health outcomes.[70] | ” |
In regards to data that relates to mental health and atheism, in December of 2003, the University of Warwick reported the following:
| “ | Dr. Stephen Joseph, from the University of Warwick, said: "Religious people seem to have a greater purpose in life, which is why they are happier. Looking at the research evidence, it seems that those who celebrate the Christian meaning of Christmas are on the whole likely to be happier.[71] | ” |

Currently, there is an ongoing debate on whether atheism was a causal factor for Friedrich Nietzsche's insanity or whether it was caused purely through disease.
Duke University has established the Center for Spirituality, Theology and Health.[72] The Duke University Center for Spirituality, Theology and Health is based in the Center for Aging at Duke and gives opportunities for scholarly trans-disciplinary conversation and the development of collaborative research projects.[73] In respect to the atheism and mental and physical health, the center offers many studies which suggest that theism is more beneficial than atheism.[74]
Currently, there is an ongoing debate regarding whether atheism was a causal factor for Friedrich Nietzsche's insanity or whether it was caused strictly by disease.[75][76][77][78] An article published on the Hong Kong Baptist University website offers the following regarding the cause of Friedrich Nietzsche's insanity:
| “ | Trying to explain what caused his insanity can only be a matter of speculation. Some people believe it was the result of a physical illness. Others interpret his suffering as that of a true prophet, almost as if he were accepting the punishment on behalf of those who could not see mankind's tendency towards self-destruction so clearly. Still others regard his final fate as a natural outcome of his philosophical outlook.[79] | ” |
Atheism and Suicide
- See main article: Atheism and suicide
Although there are recent studies relating to atheism being a causal factor for suicide, an early proponent of atheism being a causal factor for suicide was the Reverend Dr. Robert S. MacArthur.[80][81][82] In 1894, the NY Times stated the following in relation to atheism and suicide:
| “ | Dr. Martin urged that a great cause of suicide was atheism. It was, he said, a remarkable fact that where atheism prevailed most, there suicides were most numerous. In Paris, a recent census showed one suicide to every 2,700 of the population. After the publication of Paine's "Age of Reason" suicides increased.[83] | ” |
The same NY Times article quotes the Reverend Dr. MacArthur describing suicide in the following manner:
| “ | It is mean and not manly; it is dastardly and not daring. A man who involves his innocent wife and children in financial disaster and disgrace and takes his life and leaves them to bear the burden he was unwilling to bear, is a coward.[84] | ” |
In 2004, the American Journal of Psychiatry reported the following:
| “ | Religiously unaffiliated subjects had significantly more lifetime suicide attempts and more first-degree relatives who committed suicide than subjects who endorsed a religious affiliation. Unaffiliated subjects were younger, less often married, less often had children, and had less contact with family members. Furthermore, subjects with no religious affiliation perceived fewer reasons for living, particularly fewer moral objections to suicide. In terms of clinical characteristics, religiously unaffiliated subjects had more lifetime impulsivity, aggression, and past substance use disorder. No differences in the level of subjective and objective depression, hopelessness, or stressful life events were found.[85] | ” |
The website Adherents.com reported the following in respect to atheism and suicide:
| “ | Pitzer College sociologist Phil Zuckerman compiled country-by-country survey, polling and census numbers relating to atheism, agnosticism, disbelief in God and people who state they are non-religious or have no religious preference. These data were published in the chapter titled "Atheism: Contemporary Rates and Patterns" in The Cambridge Companion to Atheism, ed. by Michael Martin, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK (2005). In examining various indicators of societal health, Zuckerman concludes about suicide:"Concerning suicide rates, this is the one indicator of societal health in which religious nations fare much better than secular nations. According to the 2003 World Health Organization's report on international male suicides rates (which compared 100 countries), of the top ten nations with the highest male suicide rates, all but one (Sri Lanka) are strongly irreligious nations with high levels of atheism. It is interesting to note, however, that of the top remaining nine nations leading the world in male suicide rates, all are former Soviet/Communist nations, such as Belarus, Ukraine, and Latvia. Of the bottom ten nations with the lowest male suicide rates, all are highly religious nations with statistically insignificant levels of organic atheism."[86] | ” |
Australian online opinion writer and lecturer in ethics and philosophy at several Melbourne theological colleges, Bill Muehlenberg, in his essay The Unbearable Heaviness of Being (In a World Without God) states the following:
| “ | Announcing, and believing, that God is dead has consequences. And it is we who suffer the most for it. We cannot bear the whole universe on our shoulders. We were not meant to. We must let God be God. Only then can men be men. Only then can we find the way forward to be possible, and the burdens not insurmountable.[87] | ” |
Sigmund Freud's View of Religion

Sigmund Freud in his laboratory
Psychologist Sigmund Freud was a proponent of atheism who argued that theism was detrimental to mental health.[88] Oxford Professor Alister McGrath, author of the book The Twilight of Atheism, stated the following regarding Freud:
| “ | One of the most important criticisms that Sigmund Freud directed against religion was that it encourages unhealthy and dysfunctional outlooks on life. Having dismissed religion as an illusion, Freud went on to argue that it is a negative factor in personal development. At times, Freud's influence has been such that the elimination of a person's religious beliefs has been seen as a precondition for mental health.Freud is now a fallen idol, the fall having been all the heavier for its postponement. There is now growing awareness of the importance of spirituality in health care, both as a positive factor in relation to well-being and as an issue to which patients have a right. The "Spirituality and Healing in Medicine" conference sponsored by Harvard Medical School in 1998 brought reports that 86 percent of Americans as a whole, 99 percent of family physicians, and 94 percent of HMO professionals believe that prayer, meditation, and other spiritual and religious practices exercise a major positive role within the healing process.[89] |
O Desespero de um Evolucionista
Durante o ano de 2005 o evolucionista James Randi tentou subornar o "Smithsonian" para que estes não exibissem o filme "THE PRIVILEGED PLANET".
O filme em questão oferece uma vasta gama de evidências científicas que suportam a posição de que o universo é o resultado de design inteligente, em oposição à crença de que o universo criou-se a si próprio.
O evolucionista James Randi, "preocupado" com as ramificações de tal filme, fez o que qualquer pessoa normal faria numa situação destas: ofereceu dinheiro para que o filme não fosse exibido.
Sim, os darwinistas estão tão desesperados que a informação circule livremente que oferecem dinheiro para que as evidências contra o naturalismo não cheguem aos ouvidos das massas.
O Dr David Berlinski, um matemático e filósofo, resolveu responder ao Randi. Eis aqui a sua resposta:
...............................................................................................................................
An Open Letter to the Amazing Randi
By: David Berlinski
Discovery Institute
June 13, 2005
Dear Amazing Randi:
I just read your widely publicized letter to the Smithsonian about its decision to air The Privileged Planet, Discovery Institute's film on intelligent design. You find it “impossible to comprehend” why the Smithsonian has chosen to screen such a film. And, I see that you are willing to pay the Smithsonian Institute $20,000 so that they don’t do it.
I want you to know, you’re doing the right thing. I figure the American people are dumb as posts. Who knows what ideas a film like that could put into their heads? You haven’t seen the film either, am I right? See no evil, see no evil is what I always say.
But here’s the thing, Randi. I was sort of planning to screen the film right here in my apartment in Paris. I’ve got a little screening room I call The Smithsonian right between the bathroom and the kitchen, I sort of figured I’d invite some friends over, open a couple cans of suds, sort of kick back and enjoy. Now you fork over $20,000 to the Smithsonian not to show the film and right away I’m showing the film here in Paris — that’s just not going to work for you, if you catch my drift.
But hey, what are friends for? I mean for $20,000, I can make my screening of the The Privileged Planet go away too. An extra $10,000 and we spend the evening reading aloud from Daniel Dennett’s autobiography. I hear it’s a real snoozer, no chance at all that anyone’s going to walk away from an evening like that with poor thoughts about the cosmos or anything like that. You handle the refreshments — nothing much, some cocktail franks maybe, a few kegs of French beer — and I knock ten percent off the price. What do you say?
Now I know what you’re thinking, Randi, because to tell you the truth, I’ve been thinking the same thing. You’re thinking, hey, I’m out forty thousand seminolas to can this film in Washington DC and Paris, and right away, some yutz is going to figure it’s show time in Oklahoma or Nebraska or even in New York, and what do I do then? I’m way ahead of you on this one. I’ve talked with my buddies at the Discovery Institute and for the right kind of donation, we poleax the film completely. That’s right. It disappears itself, if you catch my drift. You get to keep the negatives, we keep the director’s cut in our safe for insurance. Is this some sort of deal, or what?
Now I know what you’re thinking because I’ve been there myself. You’re thinking, the Discovery Institute? Bunch of right-wing weirdoes, am I right? Hey, it’s not like that at all, Randi, I got to tell you. We here at the Discovery Institute, we’re businessmen, if you catch my drift. We want to do the right thing and we want to do it at the right price. Look at it this way. The right kind of donation gets you total peace of mind. You really can’t buy that kind of protection, only in this case you can.
So give me a ring, or send me a note. I’d like to tell you we take checks, but you’re a businessmen, too, am I right? It’s got to be cash. More than you’ve got lying around? Not a problem. Just give George Soros a call. Tell him it’s for a friend. Do it now.
You’ll sleep better at night.
Your admirer,
David Berlinski
PS: I write a lot of stuff for Commentary, too. For the right price, I don’t have to write anything at all. Think it over. Let me know.
David Berlinski received his Ph.D. in philosophy from Princeton University and was later a postdoctoral fellow in mathematics and molecular biology at Columbia University.
sexta-feira, junho 27, 2008
A Razão do Medo Darwinista
In the latest Gallup poll in a 26-year series asking the same questions, only 14% of Americans are chance worshippers when it comes to evolution. The other 86% believe an intelligent agent was involved. Of course the poll names the intelligent agent “God” but you know what my old pal William Shakespeare had to say about that - “a rose by any other name would smell as sweet”.
Imagine what the numbers would be like if criticism of evolution by chance & necessity were allowed into the childhood secular indoctrination program (a.k.a. public schools). No wonder the chance worshippers freak out over the thought of having their lame hypothesis discussed in an open manner. If, in the absence of criticism, they can only convince 14% of the kids how many fewer would buy what they’re selling if criticism were allowed?
........................
Conclusão:
A teoria da evolução é ensinada nas escolas publicas americanas, mas apenas 14% acreditam na versão que é ensinada lá.
O criticismo científico à teoria da evolução practicamente não existe nas escolas públicas, mas mesmo depois de décadas a indoctrinar as pessoas (com o dinheiro público) e sem ensino de nenhuma alternativa, apenas 14% dos indivíduos da nação que anualmente ganha mais prémios científicos acredita que as forças da natureza têm poder para gerar os sistemas presentes no mundo biológico.
Isto talvez explique o porquê de os darwinistas não aceitarem críticas à sua religião.
Se sem criticismo, só 14% adoram a "mãe natureza" como criadora, o que é que haveria de acontecer se as evidências científicas contra a teoria da evolução fossem apresentadas livremente?
Portanto, percebe-se o medo darwinista.
quinta-feira, junho 26, 2008
Arqueologia e a Bíblia - O Muro de Neemias
"Ficámos surpreendidos" admitiu a chefe da equipa a Drª Eilat Mazar, não deixando de notar que esta descoberta foi feita numa altura em que muitos estudiosos afirmavam que o muro nunca existiu.
(Como sempre, Deus tem a última palavra)
Aparentemente a descoberta foi acidental - o resultado de uma tentativa de salvação numa torre em perigo de cair.
A Drª Mazar é a supervisora/chefe/líder do "Institute of Archaeology at the Shalem Center", um instituto virado para a área educacional e a área de pesquisa baseado em Jerusalem.
Recentemente ela e a sua equipa voltaram a estar nas páginas dos jornais. Desta vez foi devido à descoberta de um selo em pedra durante as suas escavações me Jerusalem.
O selo em pedra tem o nome ‘Tamá’ gravado nela. "Por acaso" o Livro de Neemias também menciona ‘Tamá’. A Bíblia fala nos "descendentes de Temá" no versículo Neemias 7:55 (Hebraico תמח, às vezes transliterado para Temach, Temah or Tamah) como pertencendo ao grupo dos serviçais do templo (7:46) que voltaram do exílio na Babilónia para Jerusalém e Judá (7:6).
A Drª Mazar disse que o selo foi encontrado a uma certa distãncia da área "Opel" (ou Aphel), onde os serviçais do templo viviam durante a época de Neemias (11:21).
'O selo da familia Temá dá-nos uma ligação directa entre a arqueologia e as fontes Bíblicas, e serve de evidência para a família mencionada na Bíblia" afirmou a Drª Mazar. 'Não podemos de deixar de estar surpresos pela credibilidade das fontes Bíblicas, tal como confirmado pelo achado arqueológico.'
Sinceramente, não há razão nenhuma para se estar "surpreso" pelo facto de que a Bíblia é uma fonte histórica de confiança.
Deus falou através dos Seus Profetas (2 Pedro 1:20–21, Hebreus 1:1), Ele nunca mente (Tito 1:2), e a Bíblia confirma isso mesmo, e a Palavra de Deus pode ser confiada (2 Timóteo 3:15–17).
Conclusão:
Aquilo que Deus falou sobre o passado tem sido confirmado vez após vez pela ciência. A arqueologia tem sido uma ciência que tem, literalmente, sido uma arma evangelística poderosa.
Se o que Deus disse sobre a história de Israel e sobre outros factos, têm sido confirmados pela ciência, porque é que vamos pôr em causa logo o princípio da Bíblia? O mesmo tipo de narrativa usada por Deus no Livro de Neemias está presente na descrição da Criação. Como tal, e uma vez que históricamente a Bíblia tem sido confirmada vezes e vezes sem conta, não há razão lógica nenhuma para pôr em causa o Livro do Génesis.
Isto é tanto mais verdade quando a alternativa (evolução) é claramente uma fábula ateísta mascarada de ciência, e não está de acordo com as observações.
segunda-feira, junho 23, 2008
A Ditadura da União Europeia
"Os irlandeses não se podem opôr à vontade de 500 milhões de europeus."
Mas....quem disse que a vontade dos restantes europeus é diferente da vontade dos irlandeses? Os irlandeses ao menos tiveram a hipótese de votar. Nós nem a isso tivémos direito!
Façam o mesmo referendo aos outros 500 milhões, e depois vêmos a resposta.
Eis aqui um video da discussão parlamentar.
"Qual é a relação entre isto e o debate entre a criação e o evolucionismo?" pode-se perguntar?
Oh, apenas e só que a mesma organização ditaturial que quer forçar tratados bela guela abaixo dos europeus, é a mesma organização que diz que o criacionismo é um ataque ao direitos humanos. (Parem de rir, por favor. É tarde e os vizinhos podem ouvir, bolas!)
Sim, porque, como toda a gente sabe, os grandes violadores dos direitos humanos no século 20 eram todos firmes crentes no criacionismo Bíblico. Os "criacionistas" José Stalin, Pol Pot e Mao Tse Tung por várias vezes fizeram menção da sua fé na criação em 6 dias, e no Dilúvio Universal nos dias de Noé.
Isto para não falar no "criacionista" Hitler, que, tal como a Bíblia diz, sempre acreditou que todos os seres humanos são descendentes do mesmo pai (Adão) e da mesma mãe (Eva), e que nunca na sua vida considerou uma raça superior a outra. Se houver dúvidas disso, basta lembrar o que o Hitler fez quando o afro-americano Jesse Owens ganhou 4 medalhas nos jogos Olímpicos de 1936.
Concluindo:
Os ditadores que hoje governam a europa estão cada vez menos cuidadosos em esconder os seus sentimentos totalitários. Isto é visível não só ao nível das suas políticas mas especialmente ao nível do "controlo" da informação que eles querem fazer no que toca o debate sobre as nossas origens.
Ideologias que receiam a livre circulação de informação são ideologias que temem a verdade.
O que é que o parlamento europeu tem a esconder? Porque é que eles temem tanto o criacionismo?
sábado, junho 21, 2008
Semente Subterrada há 2000 Anos Volta à Crescer
Uma semente enterrada debaixo dos escombros da fortaleza de Herodes o Grande formou raízes e está a tornar-se numa palmeira.
Science Now reportou este facto como verificação de que sementes antigas ainda podem crescer. A National Geographic News reportou que esta germinação ultrapassa o record anterior que estava fixado em 700 anos.
A equipa de investigação israelita deu a alcunha de “Methuselah” à arvore, o nome da pessoa com maior longevidade alguma vez reportada.
Os testes rádio carbónicos efectuados em outras sementes do mesmo grupo mostrou datas entre o entrevalo 2110-1995.
Conclusão:
Esta semente esteve enterrada numa fortaleza, no quente deserto da Judeia, durante 2000 anos. Já imaginaram fazer uma máquina que dure 2000 anos? Imaginem o Rei Herodes fazer uma máquina que pudesse ser empacotada, enterrada durante 2000 anos, desempacotada, e posta funcionar outra vez. Seria uma marco da engenharia e do design.
Agora imaginem um robô minúsculo que lê códigos, pode crescer, extrair nutrientes das areias do deserto e produzir frutos doces. Espantoso!
Qual é a explicação mais lógica para a origem de tal robô minúsculo? Milhões e milhões de acidentes naturais, filtrados pela sempre atenta selecção natural, ou design? Alguém já viu uma força sem inteligência a criar máquinas biológicas? Existe alguma força da natureza capaz de criar códigos de informação?
Acho que a resposta é por demais óbvia. Claro que isto não vai convencer o ateu devoto, uma vez que para ele tudo tem que ter uma explicação naturalista, mesmo que as evidências apontem para o Criador.
Quem é que precisa de evidências quando se tem o naturalismo?
sexta-feira, junho 20, 2008
quinta-feira, junho 19, 2008
Quais São as Origens Evolutivas do Ateísmo?
Evolutionary Science: Deconstructing (Other Peoples') Religious Beliefs
 A recent study in American Scientist should ignite a blaze of research in evolutionary psychology. In Evolution, Religion, and Free Will, Gregory Graffin and William Provine report their survey of the religious beliefs of eminent evolutionary scientists. The results are striking. Evolutionary scientists hold views about God and religious belief that are radically at odds with those of most Americans. To evolutionary scientists such extreme variance from the mainstream views would normally raise fascinating questions about selection factors associated with atheist adaptation. Graffin and Provine's study should give rise to scores of papers about the evolutionary origins of atheism.
A recent study in American Scientist should ignite a blaze of research in evolutionary psychology. In Evolution, Religion, and Free Will, Gregory Graffin and William Provine report their survey of the religious beliefs of eminent evolutionary scientists. The results are striking. Evolutionary scientists hold views about God and religious belief that are radically at odds with those of most Americans. To evolutionary scientists such extreme variance from the mainstream views would normally raise fascinating questions about selection factors associated with atheist adaptation. Graffin and Provine's study should give rise to scores of papers about the evolutionary origins of atheism.
But it won't.
There's no doubt that the religious beliefs of evolutionary scientists are radically different from those of most Americans. Graffin and Provine's study, called the Cornell Evolution Project, evaluated the results of a questionnaire returned by 149 leading evolutionary scientists about their religious beliefs. Eighty percent of evolutionary scientists were strict atheists. Another six percent expressed atheist beliefs, but left some room for 'mystery'. About five percent were deists, and five percent had a more or less traditional belief in God. Religious beliefs of evolutionary scientists are the inverse of the beliefs of the American public, nearly ninety percent of whom believe in God.
Yet the authors note that the great majority of evolutionary scientists (nearly ninety percent) see no conflict between religion and evolution. Ironically, this is not because evolutionary scientists believe that religion and science represent different 'magisteria', but because they believe that religious belief is a product of evolution. The vast majority of evolutionary scientists attribute belief in God to evolutionary mechanisms. That is, they deconstruct belief in God, and imply that it is merely an adaptive trait, or an accident— a spandrel. Evolutionary scientists' own scientific opinions about the evolutionary origin of belief in God correspond quite nicely to their own personal religious disbelief.
But then what is the evolutionary origin of disbelief in God? If evolutionary scientists were unbiased in their approach to the study of religious belief, they would study the evolutionary origins of their own beliefs, as well as the origins of the beliefs of others. Despite the significant evolutionary questions raised by the adherence of a group of intelligent well-educated professionals to a fringe ideology—atheism— that has had a profound influence on the 20th century, evolutionary scientists show no interest in honest evolutionary introspection. That's surprising if their interest is genuinely scientific, but quite unsurprising if they are advancing an implicit or explicit ideological agenda with their work.
For evolutionary scientists, deconstructing religious belief is a method applied to other peoples' beliefs. Graffin and Provine, unpreturbed by this double standard and by the implications for the integrity of evolutionary science, point out the pragmatic implications of evolutionary scientists' obvious theological bias:
Senator Sam Brownback recently pointed out in his New York Times essay that some aspects of evolutionary theory are atheistic theology, disguised as science. As Graffin and Provine's study demonstrates, the evidence supporting Brownback's assertion is overwhelming.
Posted by Michael Egnor on June 23, 2007 7:34 AM
http://www.evolutionnews.org/2007/06/evolutionary_science_deconstru.htmlsegunda-feira, junho 16, 2008
Computador Mais Proximo do Cérebro
Em linguagem computacional FLOPS (ou flops) é um acrônimo que significa FLoating point Operations Per Second que, em português, quer dizer operações de ponto flutuante por segundo
| Computador Desempenho | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nome | flops | |
| megaflop | 106 | |
| gigaflop | 109 | |
| teraflop | 1012 | |
| petaflop | 1015 | |
| exaflop | 1018 | |
| zettaflop | 1021 | |
| yottaflop | 1024 | |
| xeraflop | 1027 | |

Science Daily reporta que este computador pode fazer uma coisa ainda mais espantosa:
O Roadrunner é capaz de imitar algumas das complexas reacções neurais que ocorrem no cérebro humano.
Ate hoje os computadores não têm conseguido igualar a performance humana em trabalhos visuais como detectar um veículo em aproximação numa autoestrada, ou distinguir um amigo de um estranho numa multidão de pessoas.
O Roadrunner está a mudar as coisas.
Um programa de teste chamado PetaVision tenta imitar como é que o cérebro executa a visão.
“PetaVision models the human visual system--mimicking more than 1 billion visual neurons and trillions of synapses.” Because there are about a quadrillion synapses in the human brain, an artificial brain is finally entering the ballpark of keeping up with the biological computer."
Por outras palavras, os programas feitos pelos cientistas estão-se a aproximar da superior capacidade do cérebro humano no que toca a execução de funções visuais.
Conclusão:
Foram precisas décadas de inteligência humana e engenharia para construir esta monstruosidade metálica, que só agora está a aproximar-se de UMA das operações do cérebro humano, nomeadamente, a visão. Para operar, esta máquina precisa de uma sala metálica, cabos com um circuito elétrico, arrefecimento artificial e uma equipa de administradores, sem contar com os programadores.
O nosso cérebro, por contraste, tem apenas 1,3 Kgs, está contido numa plataforma móvel, e faz muito mais do que apenas processar a visão. Mantém o controlo sobre trilhões de células, sobre o coração, pulmões, aparelho digestivo, fígado, pancreas, glandulas, sistema imunitário e muitos outros sistemas. Não só faz isto tudo inconscientemente, mas reage à audição, ao cheiro, ao sabor, ao toque, equilíbrio e a temperatura. Para além disso ele busca memórias, pensa, imagina, sente e muito mais. Isto tudo dentro de um espaço de 1350 cc.
Não é preciso ligá-lo à corrente. Não é preciso pô-lo numa área refrigerada. Podemos fazer ski, ou ir para o deserto, e até podemos nadar com ele. E o que é que ele precisa como combustível? Sardinhada e água! (ok, um pouco de vegetais também ajuda!)
O evolucionista ateu olha para o Roadrunner e fica maravilhado ("Que bela máquina!"). No entanto, o mesmo ateu olha para o bem mais eficiente e bem mais complexo cérebro humano e diz "Obviamente que ninguém fez o cérebro! É óbvio que ele é o resultado de milhões de anos de evolução não-direccionada, não-inteligente e não-pessoal!"
Pois pois.....
Deus tem um verso especialmente para aqueles que negam o óbvio:
Pois os Seus atributos invisíveis, o Seu Eterno Poder e Divindade, são claramente vistos desde a criação do mundo, sendo percebidos mediante as coisas criadas, de modo que eles são inescusáveis;
O ser humano não têm razões para negar a existência de Deus uma vez que as evidências são claramente visíveis. O grande Rei, o Rei David, não tinha telescópios nem tinha microscópios, mas ele podia olhar para si próprio e dizer "Maravilhosamente fui criado!"
O ateu evolucionista, rodeado de tecnologia, olha para a complexidade dentro de uma célula, e olha para a vastidão e ordem que há no universo e conclui que é tudo obra das forças da natureza. É tudo o resultado de forças sem inteligência.
Pois....

quarta-feira, junho 11, 2008
domingo, junho 08, 2008
Pavão e Ciência versus Darwin
O design presente na cauda do pavão, cheio de padrões que se parecem olhos, mostra todos os indícios de ter sido criado - por Um Criador.
Não é, portanto, surpresa nenhuma que Darwin tenha tido dificuldades em explicar a cauda do pavão em termos evolutivos. Para ser mais preciso, o que Darwin disse foi:
‘The sight of a feather in a peacock’s tail, whenever I gaze at it, makes me sick!’ 1
Estas foram as suas palavras exactas no ano de 1860, um ano depois de ter publicado o seu livro "Origin of Species".
Como Darwin não podia ficar "sick" (doente) eternamente, onze anos depois (1871) ele propôs a sua teoria da "selecção sexual" como forma de providenciar uma explicação naturalista (evolucionista) para as penas do pavão.
Basicamente, a ideia de Darwin era a de que as penas e os padrões presentes no pavão evoluiram (isto é, apareceram naturalmente) como resposta às escolhas das fémeas. Os pavões com as caudas mais bonitas seriam mais atraentes para as fémeas, fazendo com os que esses fossem escolhidos. Estes acasalavam mais e passavam os seus genes para a geração seguinte, incluíndo os genes da cauda atraente.
Largamente publicitados estudos foram feitos que "confirmaram" que as pavoas preferem os machos com as caudas mais atraentes. Este "facto" passou a fazer parte do "canon da biologia evolutiva".
No entanto, agora entra a ciência, e sempre que isso acontence, a evolução tem que "dar o seu lugar".
Observações detalhadas conduzidas pela equipa Mariko Takahashi (Universidade de Tóquio) coloca problemas à crença evolucionista de que as penas do pavão evoluiram em resposta ás escolhas da fémea. 3,4
O estudo não encontrou evidência alguma de que as pavoas escolhem os machos de acordo com a qualidade das caudas. Esta situação vai contra a teoria darwinista da "selecção sexual".
Contrariamente ao que diz a teoria darwinista da selecção sexual, os pesquisadores verificaram que a cauda do pavão "não é objecto a preferência sexual das pavoas".
Convém ressalvar que mesmo que as fémeas fossem atraídas pelas caudas mais bonitas, isto não explica a origem da informação genética que codifica para caudas de pavão.
Conclusão:
Darwin observou as caudas do pavão, e tentou explicá-las naturalisticamente (evolutivamente). Ele propôs a teoria da selecção sexual. A ciência observou que não existe nenhuma selecção sexual no que toca as caudas do pavão. Portanto a explicação de Darwin em relação as caudas do pavão está cientificamente refutada .
E o Criacionismo?
A Palavra de Deus é mais uma vez confirmada com os avanços da ciência.
As estruturas presentes nas caudas do pavão (beleza, ordem, elegância, informação genética e design) são um testemunho forte para o Deus Criador. Ele não tinha necessidade nenhuma de fazer as caudas do pavão bonitas, mas Ele fê-las assim para que nós soubessemos que elas foram feitas por Alguém.
Esse tipo de estruturas são sempre evidências de uma ou mais mentes por trás desses sistemas. Se encontramos essas coisas no mundo biológico, então isso está de acordo com o que a Bíblia diz, nomeadamente, que Deus criou tudo o que está nos céus, na terra e nos mares (Êxodo 20:11).
A Palavra de Deus e a ciência estão em plena harmonia.
........
(Artigo original pode ser encontrado aqui)
domingo, junho 01, 2008
sábado, maio 31, 2008
Fósseis versus Darwin
Uma das ilusões mais fortes espalhadas pelos crentes darwinistas na arena pública é a de que o registo fóssil é evidência sólida de que as formas de vida estão relacionadas umas com as outras por descendência comum. Por sua vez, segundo reza o mito darwinista, essa linhagem é o resultado de forças não-guiadas, não-direccionadas, não-inteligentes, e não-pessoais.
O problema começa quando se começam a investigar os fósseis e se vê que, apesar de terem passado mais de 100 anos, os fósseis estão mais de acordo com a Criação do que com o darwinismo.
O evolucionista David Raup escreveu em 1979:
“O conhecimento do registo fóssil expandiu-se muito nestes 120 anos depois de Darwin…. Ironicamente, nós temos hoje menos exemplos de transições evolucionarias do que tinhamos no tempo de Charles Darwin (1).”
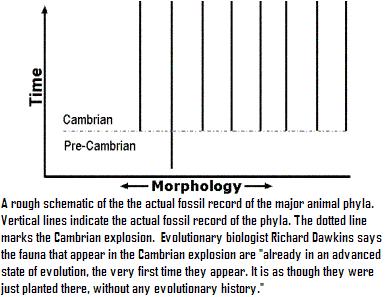
Uma das áreas onde a teoria da evolução está claramente contra os dados observáveis é no que toca à explosão do Período Câmbrico.
Um livro escolar diz:
“A maior parte do filo animal que está representado no registo fóssil aparece “completamente formado”, no período Câmbrico há cerca de 550 milhões de anos atrás…. O registo fóssil não serve portanto de ajuda no que respeita às origens e à diversificação dos vários filo animal” (2)
O problema é que esta exlosão não é a única. Foi observado no registo fóssil que há a “explosão” dos peixes, a “explosão” das plantas, a “explosão” das áves e até mesmo a “explosão” dos mamíferos. (Só nos falta mesmo é a explosão da teoria da evolução!)
Isto é exactamente o contrário do que se poderia prevêr se a evolução tivesse acontecido.
A evolução “prevê” uma continuidade e uma transição das formas de vida de um para as outras. Se isto fosse verdade, então o registo fóssil estaria inundado das espécies intermédias (aqueles que ainda não são o “ponto final”, mas já deixaram de ser o “ponto inicial”).
O que nós observamos é exactamente o contrário. Nós observamos o aparecimento abrupto (”explosivo”) das formas de vida, exactamente o que seria de prevêr se a Criação tivesse acontecido.
Conclusão:
Mais uma vez se vê que aquilo que os darwinistas esperavam da ciência falhou, e que essa mesma ciência está de acordo com o que Deus disse no Livro do Génesis.
………………………………….
1. David Raup, “Conflicts Between Darwin and Paleontology”, Field Museum of Natural History Bulletin, Vol. 50 (1) (1979).
2. R.S.K. Barnes, P. Calow & P.J.W. Olive, The Invertebrates: A New Synthesis, pages 9–10 (3rd ed., Blackwell Sci. Publications, 2001).
quinta-feira, maio 29, 2008
A FRAGILIDADE DE UMA CRENÇA
A FRAGILIDADE DE UMA CRENÇA João César das Nevesprofessor
universitárionaohaalmocosgratis@fcee.ucp.pt
A vida pública é hoje ateia ou agnóstica. Ouve-se muito criticar a tolice e o delírio das religiões, mas raramente se refere a fragilidade intelectual da própria atitude ateísta que, com todo o respeito, é muito inconsistente.
Recusar Deus é uma crença como as outras. No fundo trata-se de ter fé na ausência divina. Mas esta crença considera-se a si mesma lógica e natural. A Antropologia e Sociologia sérias mostram o oposto: a religiosidade é o normal em todas as culturas e épocas.
O ateísmo é uma construção tardia e artificial de elites, sobretudo desde o Iluminismo. Mantido em ínfima minoria, agora está em clara decadência. Vendo- -lhe a lógica interna, percebe-se porquê.
O agnosticismo, hoje variante dominante, justificar-se-ia se a existência de Deus fosse inconsequente e negligenciável.
Mas ignorar a possibilidade de Deus é como desinteressar-se da existência do pai, benfeitor ou patrão, senhorio ou polícia. E se Ele aparece? Os verdadeiros agnósticos, com reais dúvidas, são poucos porque a maioria assume a resposta negativa implícita, vivendo um ateísmo disfarçado.
O disfarce evita as dificuldades conceptuais e empíricas do ateísmo aberto, superiores a qualquer religião ou ideologia.A dificuldade mais visível vem da existência da realidade. Porque há algo em vez de nada? Porque existe ordem, não caos?
A resposta ateia era recusar a questão, porque o universo sempre existira assim, mas a teoria do Big Bang explodiu essa certeza e deu solidez científica ao facto da Criação.Eu e o mundo, as coisas, pessoas e outros seres não existiam e passaram a existir. E existem de forma harmónica e coerente.
A realidade é um infinito mosaico de minúcia e complexidade incompreensíveis. A ciência demonstrou que variações infinitesimais de parâmetros fundamentais, das forças do núcleo atómico à densidade do universo, torná-lo-iam impossível. Uma obra supõe um autor. Falar em leis da natureza apenas recua a questão para a origem dessas leis. Seria supina tolice supor um relógio surgindo perfeito das forças fortuitas da geologia e erosão.
Um cérebro, muito mais complexo, quem o fez?A resposta ateia tem de ser que o acaso de milhões de anos conduziu de uma explosão ao sorriso da minha filha. Ou o acaso é Deus, e o ateísmo nega-se, ou essa explicação é muito mais frágil que supor um Autor para a cosmos.
Não tem certamente motivos científicos, ou até razoáveis, a recusa da hipótese plausível de um Criador inteligente. Muito inteligente.Uma segunda dificuldade vem de dentro. Todos os humanos sentem em si uma ânsia de justiça e verdade, um sentido de bem e mal.
Os actuais direitos universais apenas corporizam essa herança original e nela se justificam. Alguns valores são comuns, na enorme variedade de culturas e hábitos. Essa mesma variedade confirma que tal não pode vir de construções históricas e sociais, porque subjaz a todas.A violação da lei moral apenas confirma a sua existência.
Muitos conseguem suprimir em si esta busca da justiça (embora a sintam quando vítimas), mas o trabalho que dá apagá-la revela a inscrição na própria identidade da raça. Uma lei implica um legislador. Como podem meros atómos de carbono, aglomerados em aminoácidos e evoluindo pela selecção natural, gritar que salário digno é valor universal?
O terceiro e pior obstáculo do ateísmo é a ausência de finalidade. Para o ateu este universo, sem origem nem orientação, também não tem propósito. Bons e maus têm o mesmo destino vazio. Saber que vivemos num mundo que se dirige à morte e ao nada faz de nós os mais infelizes dos seres.
Se Deus não existe não existem o bem, a moral, a própria razão. Esta crueldade ontológica é tão avassaladora que poucos que a afirmam a enfrentam com honestidade.A fragilidade lógica do ateísmo é pouco relevante por ser um fenómeno elitista ocidental contemporâneo que, exportado à força pelo marxismo, está em extinção.
A única questão interessante é saber porque coisas tão simples foram escondidas aos sábios e inteligentes e reveladas aos pequeninos.
terça-feira, maio 27, 2008
"Calamidades Afastam as Pessoas de Deus"
*"Se Deus é Bom e Todo Poderoso, como é que se explica a existência do Mal no mundo que Ele fez?!!"
O que se poderia deduzir deste dilema é que em lugares onde há muito sofrimento a fé em Deus seria a última coisa na mente das pessoas.
Não é o que se está a passar na China depois da calamidade que afectou Mianyang (perto do epicentro do terremoto). Os membros de uma das maiores igrejas da cidade juntaram-se para cantar "All Hail the Power of Jesus' Name!"

domingo, maio 25, 2008
Walter Martin e o Mundo do Ocultismo
Esta é a parte 6 da apresentação do falecido Reverendo Walter Martin sobre o mundo do ocultismo.
Achei por bem pôr aqui o segmento 6 uma vez que há pessoas que não acreditam no mundo sobrenatural.
sábado, maio 24, 2008
Milagres Não Acontecem! (Excepto Quando Acontecem)
Val Thomas, que vive em "West Virginia", está ser chamada de um milagre médico depois de ter sofrido dois ataques do coração e sem ter ondas cerebrais durante mais de 17 horas.
O coração da srª Val Thomas parou cerca da 1:30am de Sábado e os doutores disseram que ela não tinha pulso. "Rigor mortis" começou a tomar efeito, e ela foi posta numa máquina respiratória.
"A pele já tinha começado a endurecer, e os dedos encaracolaram" o filho da srª Val Thomas, Jim, disse à NewsNet5.com. "A morte tinha tinha-se estabelecido."
A srª Val Thomas, de 59 anos de idade, foi rapidamente levada ao hospital "West Virginia", onde ela foi posta numa máquina especial feita para induzir a "hipotermia". Os doutores disseram que isto haveria de causar a que o corpo dela baixasse de temperatura durante 24 horas antes de eles poderem começar a aquecê-la outra vez.
No entanto, o coração da srª Thomas parou outra vez depois do procedimento induzido.
A família disse adeus e os tubos que ligavam a srª Thomas à máquina foram desligados. No entanto, ela ficou ligada ao ventilador uma vez que a possibilidade de orgãos serem doados estava a ser discutida.
No entanto, a srª Val Thomas acordou 10 minutos depois e começou a falar.
O filho da srª Val Thomas disse que a enfermeira pediu desculpas, e que a sua Mãe respondeu "That’s OK, honey, that’s OK."
Val Thomas foi transferida para a "Cleveland Clinic" de modo a que os especialistas a pudessem analisar, mas os doutores disseram que não há nada de errado nela.
"Eu sei que Deus tem algo preparado para mim, um outro propósito", disse a srª Val Thomas. "Eu não sei qual é, mas tenho a certeza que Ele vai-me dizer."
..........................................................................................................
Eu sei o que os ateus residentes estão a pensar:
1. "Isso é tudo mentira! Essa história nunca aconteceu!"
2. "De certeza que há uma explicação natural para tudo isso!"
3. "É mais uma invenção criacionista!!"
etc, etc
As perguntas que eu gostaria de fazer são: porque é que assumes à partida que coisas como estas *nunca* podem acontecer? Será que essa tua posição não é o resultado de uma coisa que aconteceu antes, nomeadamente, a crença no naturalismo? E se essa é a tua posição filosófica, então não és propriamente neutro na análise das evidências, certo?
Eu não quero dizer com isto que o evento reportado em cima não vá ser um dia desmascarado, e mostrado ser ou uma fraude, ou um evento com uma explicação natural. A questão é que, como naturalista, a partir do momento em que começaste a lêr a história, e começaste a vêr as insuficiências da explicações naturalistas, tu imediatamente assumiste que a história é falsa. E porquê? Porque, se a historia fôr verdadeira, os contornos e as implicações apontam para algo que vai para além da forças da natureza, e tu, como naturalista, não podes aceitar isso. Como tal "suprimes" as evidências em favor da tua posição filosófica.
Voltanto para o tema do blog, será que, no que toca ao debate "Criação vs Evolução", tu não fazes o mesmo, nomeadamente, suprimir as evidências que apontam para além do naturalismo? Será que, ao olhares para o assombroso código genético, para a sua estrutura, elegância, lógica e design, tu não suprimes o que está bem patente (criação), e aceitas que este código TEM que ter uma origem naturalista? Este código tem que ter uma origem naturalista, não porque haja evidências que suportem essa crença, mas porque se o código tem uma origem inteligente, Essa Inteligência é Sobrenatural.
Talvez a mesma razão que te faz vêr à priori que o evento reportado em cima "tem que ser falso" é a mesma razão que te leva a rejeitar a Criação, e a aceitar a crença de que o mundo biológico é o resultado das forças da natureza.
quarta-feira, maio 21, 2008
Tua Palavra é Verdade - A Importância de Génesis
A doutrina da criação é fundamental para a Igreja Cristã tendo em vista que as grandes doutrinas do Cristianismo estão patentes em eventos documentos nos primeiros capítulos do Livro de Génesis.
Entre estas doutrinas estão:
1. A Natureza de Deus, incluindo o Seu Poder e Bondade
2. A natureza do Homem, criado à Imagem de Deus mas estando presentemente num estado de "caído", por causa do pecado
3. A natureza e as consequências do pecado
4. A natureza do casamento
5. A origem da morte como castigo pelo pecado, e [a morte] como uma inimiga
6. A necessidade de Um Salvador para resgatar o Homem do pecado
7. A origem e o significado do trabalho e do dia semanal de descanço.
8. A relação entre o Homem e o resto da Criação, agora debaixo da maldição do Pecado.
9. e muito mais
.....................
O que imediatamente salta à vista é o quão importante o Livro do Génesis é para a Teologia Cristã. É devido a isso que os ateus e cépticos em geral tem investido tempo e dinheiro (público) para desacreditar o Livro do Génesis. Eles sabem que se o Livro do Génesis for desacreditado, tudo aquilo sobre o qual assenta cai por terra.
Mas graças a Deus que nenhuma observação contradiz a Palavra do Criador. Tudo aquilo que o Criador diz em Génesis é confirmado, ou está de acordo com a ciência moderna. Desde o facto que os animais reproduzem-se segundo o seu "tipo", passando pelo Grande Dilúvio de Noé, acabando na Dispersão, os dados empíricos estão em sintonia com a Bíblia.
Não há razões científicas para se rejeitar a Bíblia
"A Tua Palavra é Verdade" - João 17:17
sábado, maio 10, 2008
Criacionistas e Descobertas Científicas
Lembrem-se destas descobertas científicas da próxima vez que os darwinistas contrapuserem "cientistas" e "criacionistas" como forma de implicar que os primeiros estão em oposição aos segundos.
http://creationontheweb.com/content/view/5620/
- The creationist Robert Boyle (1627–1691) fathered modern chemistry and demolished the Aristotelian four-elements theory. He also funded lectures to defend Christianity and sponsored missionaries and Bible translation work.
- Cell phones depend on electromagnetic radiation theory, which was pioneered by creationist James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879)
- Computing machines were invented by Charles Babbage (1791–1871), who was not a biblical creationist but was a creationist in the broad sense. He ‘believed that the study of the works of nature with scientific precision, was a necessary and indispensable preparation to the understanding and interpreting their testimony of the wisdom and goodness of their Divine Author.’
- The creationist brothers Orville (1871–1948) and Wilbur Wright (1867–1912) invented the airplane after studying God’s design of birds.
- The theory of planetary orbits was invented by Johannes Kepler (1571–1630), famous for claiming that his discoveries were ‘thinking God’s thoughts after him’. Kepler also calculated a creation date of 3992 bc, close to Ussher’s
. - The theory of gravity and the laws of motion, essential for the moon landings, was discovered by the creationist Isaac Newton (1642/3–1727).
- The moon landing program was headed by Wernher von Braun (1912–1977), who believed in a designer and opposed evolution. And a biblical creationist, James Irwin (1930–1991), walked on the moon. See also Exploring the heavens: Interview with NASA scientist Michael Tigges
A evolução da Evolução
‘It must be significant that nearly all the evolutionary stories I learned as a student, from Trueman’s Ostrea/Gryphaea to Carruthers’ Zaphrentis delanouei, have now been “debunked”. Similarly, my own experinece [sic] of more than twenty years looking for evolutionary lineages among the Mesozoic Brachiopoda has proved them equally elusive.’
Ager, D.V., The nature of the fossil record, Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association, 87(2):131–160, 1976
quarta-feira, maio 07, 2008
Eugenics and the Development of Nazi Race Policy
Eugenics and the Development of Nazi Race Policy
JERRY BERGMAN
NWT CollegeRoute 1, Box 246AArchbold, Ohio 43502
From: PSCF 44 (June 1992): 109-124.
A central government policy of the Hitler administration was the breeding of a "superior race." This required, at the very least, preventing the "inferior races" from mixing with "superior" ones in order to reduce contamination of the latter's gene pool. The "superior race" belief is based on the theory of group inequality within each species, a major presumption and requirement of Darwin's original "survival of the fittest" theory. A review of the writings of Hitler and contemporary German biologists finds that Darwin's theory and writings had a major influence upon Nazi policies. Hitler believed that the human gene pool could be improved by selective breeding, using the same techniques that farmers used to breed a superior strain of cattle. In the formulation of his racial policies, he relied heavily upon the Darwinian evolution model, especially the elaborations by Spencer and Haeckel. They culminated in the "final solution," the extermination of approximately six million Jews and four million other people who belonged to what German scientists judged were "inferior races."
The concept that "all men are created equal" and the egalitarian ideal which has dominated American ideology for the past thirty years, and to a lesser degree since the founding of our country, has not been universal among nations and cultures (Tobach et al. 1974). The Germans' belief that they were a superior race had many sources, a major one being the social Darwinian eugenics movement, especially its crude survival of the fittest world view (Stein 1988, Clark 1953). As Lappe noted:
Although the idea of improving the hereditary quality of the race is at least as old as Plato's Republic, modern eugenics thought arose only in the nineteenth century. The emergence of interest in eugenics during that century had multiple roots. The most important was the theory of evolution, for Francis Galton's ideas on eugenics--and it was he who created the term "eugenics"--were a direct logical outgrowth of the scientific doctrine elaborated by his cousin, Charles Darwin (1978, 457).
Eugenics' all important impact on Nazi policy can be evaluated accurately by an examination of the extant documents, writings, and artifacts produced by Germany's twentieth century Nazi movement. Historical documents show that Nazi governmental policy was openly influenced by evolution, the zeitgeist of both science and educated society of the time (Stein 1988, Haller 1971, Keith 1946, 230). The Nazi treatment of Jews and the other "races" that their science concluded were "inferior" was largely a result of their belief that the source of biological evolution was a set of proven techniques available to scientists to significantly improve humankind. As Tenenbaum noted:
the political philosophy of the... German State, was built on the ideas of struggle, selection, and survival of the fittest, all notions and observations arrived at... by Darwin... but already in luxuriant bud in the German social philosophy of the nineteenth century.... Thus developed the doctrine of Germany's inherent right to rule the world on the basis of superior strength... of a "hammer and anvil" relationship between the Reich and the weaker nations (1956, 211).
Implementation of Nazi Race Theories
The means of evolution are drawn primarily from the process of mutations, which are then selected by natural selection. Favored individuals will be more likely to survive and increase in number, forming new races while the "weaker" ones will die off. This process, once called raciation but labeled speciation today, is the source of evolution which, in theory, continues forever. If every member of a species were fully equal, there would be nothing to select from, and evolution for that species would stop. Evolution is based on the acquiring of unique traits, whether through mutations or other means, that enable those possessing them to better survive adverse conditions than those who don't.
According to evolution theory, some people (even if it is only one person) will inherit a mutation which will be passed on and which will enable them to survive at a higher rate than those without that trait. These differences will always gradually produce new races, some of which have an advantage in terms of survival. These are the superior, i.e., the more evolved, races. When that trait eventually spreads throughout the entire race, because of the survival advantage it confers on those endowed with it, a new and "higher level" of animal will exist. Hitler and the Nazi party claimed that they were trying to apply this accepted science to society. And "the core idea of Darwinism is not evolution, but selection. Evolution... describes the results of selection" (Stein 1988, 53). Hitler stressed that "we [the Nazis] must understand, and cooperate with science":
In 1937, while Mengele was still in residence [for his M. D. degree], Otmar von Verschuer published an article in which he said, "Hitler is the first statesman who has come to recognize hereditary biological and race hygiene and make it a leading principle of statesmanship." Two years later von Verschuer announced: "We specialists of race hygiene are happy to have witnessed that the work normally associated with the scientific laboratories or the academic study room has extended into the life of our people" (Astor 1985, 23).
Darwin's evolutionary ideas were exported into Germany almost immediately. The first language into which his writings were translated--only a year after The Origin of Species was published--was German. Darwinian evolution was not only championed in Germany more than most other countries, but it was more influential on German state policy. Gasman (1971, xiii) concluded that
[i]n no other country... did the ideas of Darwinism develop as... the total explanation of the world as [it did] in Germany... [or insist] on the literal transfer of the laws of biology [as interpreted by evolution] to the social realm.
This path was started at the 1863 Congress of German Naturalists. At this meeting, one of evolutions' leading proponents and writers, Ernest Haeckel, "a respected professor of zoology" at the University of Jena, first forcefully presented the views which commenced his four decade long role as "Darwin's chief apostle" (Stein 1988, 54). He was especially active in spreading "social Darwinism,"--the application of Darwinian theory to society in order to explain the historical and social development of civilizations, specifically why some were advanced and others remained primitive. But, as Gould (1977, 77-78) concluded,
... Haeckel's greatest influence was, ultimately, in another, tragic direction--national socialism [Nazism]. His evolutionary racism; his call to the German people for racial purity and unflinching devotion to... his belief that harsh, inexorable laws of evolution ruled human civilization and nature alike, conferring upon favored races the right to dominate others.... His brave words about objective science--all contributed to the rise of Nazism. The Monist League that he had founded and led... made a comfortable transition to active support for Hitler.
Aside from Haeckel, the person most influential in helping the spread of Darwin's ideas in Germany was Houston Chamberlain, the son of a British Admiral and a German mother. In 1899 he published The Foundations of the 19th Century, which concluded that Darwinism had proved that the Germans were superior to all other races (Weindling 1989). Germans were the "foundation" of our society because they produced the industrial world. Chamberlain quoted extensively from Darwin, noting that the latter stressed that a major difference between apes and humans was brain size. The brain, he stressed, is of far more importance than any other body structure in measuring human evolution progress. The larger the brain capacity, it was then believed, the higher the intelligence. Chamberlain also was interested in phrenology, the now discredited science of determining personality traits by examining and measuring the shape and size of the bumps on one's skull (Jacquerd 1984). Certain traits, the phrenologists reasoned, were located in specific parts of the brain, and if one had developed some trait to an exceptional degree, a "bump" would exist in the appropriate place. Lastly, they concluded that the configuration of the brain and other physical traits can be used to distinguish not only humans from monkeys, but also to rank the races. This idea received wide support from
... the German academic and scientific communities... who helped prepare the way for national socialist biopolicies.... Beginning in the 1890s with the work of Otto Ammon on cephalic indexes and other such scientific proof of Aryan superiority, much German anthropology, especially the most scientific branch, physical anthropology... [concluded that] If humankind evolved through natural selection... then it was obvious that the races of humankind must be arranged hierarchically along the ladder of evolution.... there is little doubt that the anthropologists who discovered all the measurable divergent physical, psychological, and mental characteristics of the various races thought they were scientific. And so did the general public (Stein 1988, 57).
Chamberlain concluded that Darwinism had proved that the Germans were superior to all other races.
The inequality doctrine, although an integral part of German philosophy for years, reached its apex under the Hitler regime, and obtained its chief intellectual support from established science (Weiss 1988, Aycoberry 1981). Ernst Haeckel taught that "the morphological differences between two generally recognized species--for example sheep and goats--are much less important than those... between a Hottentot and a man of the Teutonic race" (1876, 434). And that the Germans have evolved the "furthest from the common form of apelike men [and outstripped]... all others in the career of civilization" and will be the race to bring humankind up to a "new period of higher mental development" (1876, 332). This was true, not only mentally but physically, because evolution achieves "symmetry of all parts, and equal development which we call the type of perfect human beauty" (1876, 321).
The inequality doctrine, although an integral part of German philosophy for years, reached its apex under the Hitler regime, and obtained its chief intellectual support from established science.
The lesser races were both inferior and worth less: "woolly-haired" peoples, he concluded, are "incapable of a true inner culture or of a higher mental development... no woolly-haired nation has ever had an important history" (1876, 10). Haeckel even argued that, since "the lower races--such as the Veddahs or Australian Negroes--are psychologically nearer to the mammals--apes and dogs--than to the civilized European, we must, therefore, assign a totally different value to their lives" (1905, 390). And Stein notes that this was not a minority or an extreme view: "Haeckel was the respected scientist; the views of his followers were often more extreme" (Stein 1988, 56).
As a race above all others, the Aryans believed that their evolutionary superiority gave them not only the right, but the duty, to subjugate all others. And race was no minor plank of the Nazi philosophy: Tenenbaum (1956,211-212) concluded that they
incorporated the... theory of evolution in their political system, with nothing left out.... Their political dictionary was replete with words like... struggle, selection, and extinction (Ausmerzen). The syllogism of their logic was clearly stated: The world is a jungle in which different nations struggle for space. The stronger win, the weaker die or are killed. In the 1933 Nuremberg party rally, Hitler proclaimed that "higher race subjects to itself a lower race... a right which we see in nature and which can be regarded as the sole conceivable right because [it was] founded on reason [of evolution]" (Quoted from The Nuremberg Trials, Vol. 14, pg. 279).
The Nazis believed that they must "direct evolution" to advance the human race by isolating the "inferior races" to prevent them from further contaminating the "Aryan" gene pool.
The Nazis believed that, instead of permitting natural forces and chance to produce what it may, they must "direct evolution" to advance the human race. To achieve this, their first step was to isolate the "inferior races" to prevent them from further contaminating the "Aryan" gene pool (Poliakov 1974). The widespread public support for this policy was a result of the common belief of the educated classes that it was scientifically proven that certain races were genetically inferior. The government was simply applying, as part of their plan for a better society, what they believed was proven science to produce a superior race of humans: "The business of the corporate state was eugenics or artificial selection--politics applied to biology" (Stein 1988, 56). In Hitler's writings, humankind were biological "animals" to whom the genetics learned from livestock breeding could be applied. As early as 1925, in Chapter 4 of Mein Kampf, Hitler outlined his view that science, specifically the Darwinian natural selection struggle, was the only basis for a successful German national policy that the very title of his most famous work--in English My Struggle--alluded to. As Clark (1953, 115) concluded,
Adolf Hitler's mind was captivated by evolutionary teaching--probably since the time he was a boy. Evolutionary ideas--quite undisguised--lie at the basis of all that is worst in Mein Kampf--and in his public speeches.... Hitler reasoned... that a higher race would always conquer a lower.
And Hickman (1983, 51-52) adds that:
It is perhaps no coincidence that Adolph Hitler was a firm believer in and preacher of evolutionism. Whatever the deeper, profound complexities of his psychosis, it is certain that [the concept of struggle was important because]... his book, Mein Kampf, clearly set forth a number of evolutionary ideas, particularly those emphasizing struggle, survival of the fittest and the extermination of the weak to produce a better society.
And the belief that evolution can be directed by scientists to produce a "superior race," as Tenenbaum (1956, vii) noted, was the central leitmotif of Nazism:
There were many other sources from which Nazism drew its ideological fire-water. But in that concatenation of ideas and nightmares which made up the... social policies of the Nazi state, and to a considerable extent its military policies as well, can be most clearly comprehended in the light of its vast racial program.
The Nazi view on race and Darwinian evolution was a major part of the fatal combination which produced the holocaust and World War II:
One of the central planks in Nazi theory and doctrine was... evolutionary theory [and]... that all biology had evolved... upward, and that... less evolved types... should be actively eradicated [and]... that natural selection could and should be actively aided. [T]herefore [the Nazis] instituted political measures to eradicate... Jews, and... blacks, whom they considered... [less evolved] (Wilder-Smith 1982, 27).
Hitler's views are rather straightforward German social Darwinism of a type widely known and accepted throughout Germany and which, more importantly, was considered by most Germans, scientists included, to be scientifically true.
Terms such as "superior race," "lower human types," "race contamination," "pollution of the race," and evolution itself (entwicklung) were often used by Hitler and other Nazis leaders. Hitler's race views were not from fringe science, as often claimed, but rather,
Hitler's views are rather straightforward German social Darwinism of a type widely known and accepted throughout Germany and which, more importantly, was considered by most Germans, scientists included, to be scientifically true. More recent scholarship on national socialism and Hitler has begun to realize that... [Darwin's theory] was the specific characteristic of Nazism. National socialist "biopolicy," [was] a policy based on a mystical-biological belief in radical inequality, a monistic, antitranscendent moral nihilism based on the eternal struggle for existence and the survival of the fittest as the law of nature, and the consequent use of state power for a public policy of natural selection (Stein 1988, 51).
Hitler: the Nazis "are barbarians! We want to be barbarians. It is an honorable title, [for by it] we shall rejuvenate the world... "
The philosophy that we can control and even propel evolution to produce a "higher level" of human is repeatedly echoed in the writings and speeches of prominent Nazis (Jackel 1972). Accomplishing this goal required ruthlessly eliminating the less fit by openly barbarian behavior:
The basic outline of German social Darwinism [was that]... man was merely a part of nature with no special transcendent qualities or special humanness. On the other hand, the Germans were members of a biologically superior community... politics was merely the straightforward application of the laws of biology. In essence, Haeckel and his fellow social Darwinists advanced the ideas that were to become the core assumptions of national socialism... The business of the corporate state was eugenics or artificial selection... (Stein 1988, 56)
Rauschning (1939) quoted Hitler as stating that the Nazis "are barbarians! We want to be barbarians. It is an honorable title, [for by it] we shall rejuvenate the world... " By this means, as Keith (1946, 230) concluded, Hitler "consciously sought to make the practice of Germany conform to the theory of evolution." As Humber (1987, ii) notes, Hitler believed that Negroes were
... "monstrosities halfway between man and ape" and lamented the fact of Christians going to "Central Africa" to set up "Negro missions," resulting in the turning of "healthy... human beings into a rotten brood of bastards." In his chapter entitled "Nation and Race," he said, "The stronger must dominate and not blend with the weaker, thus sacrificing his own greatness. Only the born weakling can view this as cruel, but he, after all, is only a weak and limited man; for if this law did not prevail, any conceivable higher development (Hoherentwicklung) of organic living beings would be unthinkable." A few pages later, he said, "Those who want to live, let them fight, and those who do not want to fight in this world of eternal struggle do not deserve to live."
Many of Hitler's top aides held similar beliefs. Hoess was "particularly interested in books on 'racial' theories, heredity and ethnological works." His race beliefs guided his management policy in the various concentration camps that he was head of, including Auschwitz. He restructured this former forced labor camp into an evolution laboratory. The inmates in Auschwitz were "no longer persons... [but] simply goods to be processed in the gigantic death-factory he had organized" (Rudorff 1969, 240).
Caring for the weak, the sick, lame, old, or poor was all directly counter to the chief driving force of evolution--the survival of the fittest, and death of the unfit. This meant that the weak must be eradicated for the benefit of the race as a whole. The Nazi Party did not view these policies as wrong or even inhumane. It openly "prided itself on its scientific ideology and modern view of the world" (Gasman 1971). Given their wholesale acceptance of evolution, their "ideas of class and race... and determinism, may well [be]... inescapable" (Barzum 1958, xx).
Caring for the weak, the sick, lame, old, or poor was all directly counter to the chief driving force of evolution--the survival of the fittest, and death of the unfit.
The Nazis were not superficial in their application of what became known as "racial hygiene." Prior to 1933, the German scientists published thirteen scientific journals devoted to racial hygiene and there were over thirty institutions, many connected with universities or research centers, devoted to "racial science" (Proctor 1988). When the Nazis were in power, something like 150 scientific journals, many of which are still highly respected, dealt with racial hygiene and allied fields (Weindling 1989). Enormous files of data were kept on the races, much of which was analyzed and used for research papers published in various German and other journals. In 1927, The Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Anthropology, Human Genetics, and Eugenics was established. Although much of the research there was related to the field of eugenics, researchers also studied a wide variety of topics including venereal disease and alcohol.
The German eugenists relied heavily upon the work done in Britain and America. Franz Bumm, the President of the Reich Health Office, "noted that the value of eugenics research had been convincingly demonstrated in the United States, where anthropological statistics had been gathered from two million men recruited for the American Armed Forces" (Proctor 1988, 40). The various institutes began to research the persistence of various "primitive racial traits" in various races in and outside of Germany. They found much evidence of "Cro magnon racial type in certain populations, and presumably also Neanderthal." Like the American and British counterparts, the German Racial Hygiene Institutes and the professors at various universities began to discover genetic evidence for virtually every malady of humankind from criminality to hernias, and even divorce, with researchers adding a few original problems of their own, such as "loving to sail on water." They saw their work as a noble effort to continue "Darwin's attempts to elucidate the origin of species" (Proctor 1988, 291).
The various institutes began to research the persistence of various "primitive racial traits" in various races in and outside of Germany.
The core concept of the survival of the fittest philosophy, the observation that all animals and plants contain a tremendous amount of genetic variety, and that in certain environmental situations some of these differences may have an advantage in survival, and others may be at a disadvantage, has been well documented. The best example is artificial selection, where breeders select the male and the female with the maximum trait that they are concerned with and then, from the offspring, again select the members which maximize that trait. Breeders using these techniques have been able to breed a wide variety of plants and animals. Breeding for certain traits, though, invariably causes the loss of other traits. Consequently, in plant and animal breeding a trade-off occur: some traits are gained, but others are lost. Thus cows are bred either for dairy use or else for meat. The theory that the German eugenists had developed was thus poorly conceived, and inadequately considered enormous amounts of data and the implications of the tremendous amounts of biological diversity which we now know exist.
Some members of the scientific community do not want to share the blame for what happened and try to justify what Nazi Germany did. The most common claim is that the German academics were coerced into accepting racist ideas. Several recent studies, including Weindling (1989) and Proctor (1988), persuasively argue that this was not the case. The limited coercion that occurred was often from the scientific community, rather than the German political force "imposing its will on an apolitical scientific community" (Proctor 1988, 5; see also Wertham 1966). The Nazis forced the dismissal of many German academics from their posts, but many were Jews, and most were dismissed for reasons not related to their opposition to eugenics. Proctor's important study eloquently argued that Nazis are
commonly portrayed... as fanatic, half crazed criminals conducting their evil plans with as much reason or sense as 1930s television gangsters. This is a false impression for a number of reasons, but primarily because it underestimates the degree to which large numbers of intellectuals, often leaders in their field, were willing and eager to serve the Nazi regime. Evidence presented in the [Nuremberg] trials reveals the involvement of doctors in a massive program for the extermination of "lives not worth living," including, first, infants with inheritable defects, and later, handicapped children and patients of psychiatric institutions, and finally, entire populations of "unwanted races" (1988, 5-6) [Emphasis mine].
"Biological arguments for racism... increased by order of magnitude following the acceptance of evolutionary theory" by scientists in most nations.
As Gould (1977, 127) concluded, "Biological arguments for racism... increased by order of magnitude following the acceptance of evolutionary theory" by scientists in most nations. Chamberlain (1899) was one of the first popular German writers to use evolution to argue for the claim that the Germans were innately biologically superior to all other races and peoples, including the Persians, Greeks, and especially the "parasitic semites" whom he branded as a "race of inferior peoples." Darwin interpreted evolution of homo sapiens as principally due to brain improvements, as shown by the much larger brain case in higher primates, and especially by the apex brain found in humans. Chamberlain picked up on this, concluding that human evolutionary differences were thus reflected in skull differences, primarily its shape and size, but also all of those traits which have historically identified human races (skin color, nose, lip and eye shape among others). He utilized as evidence for his theory not only physical anthropology and Darwinian evolution, but also the then fashionable "science" of phrenology, and
Chamberlain's racial explanation for human history was only one of the many intellectual syntheses produced in the latter half of the Nineteenth Century. Most of the "isms" which have profoundly influenced the Twentieth Century have their genesis in these decades (Schleunes 1970, 30).
Social Darwinism was thus extremely influential in the development of the racism based on physical traits that flourished in the late 19th century Germany and elsewhere.
Social Darwinism was thus extremely influential in the development of the racism based on physical traits that flourished in the late 19th century Germany and elsewhere. These racist theories closely followed the spread of Darwinian evolution, which had a wide following in Germany almost immediately after the publication of the German edition of The Origin of Species (Schleunes 1970, Cohn 1981). Although racists also relied on phrenologists for support, both phrenology and social Darwinism obtained their rational, if not their primary, basis from evolution (Davies 1955). Also used for support were comparisons of various cultures which were assumed to be a product of racial superiority (not the reverse). They concluded that inferior races produced inferior cultures, and only superior races produced superior cultures (Hooton 1941). Hence, Schleunes (1970) notes that racism came into scientific repute through its solid link with the "third great synthesis of the Nineteenth Century," the Darwinian theory of evolution and the survival of the fittest world view.
These "scientific" views about race that then existed in the western world, especially Nazi Germany, were clearly evident even in America, as is apparent from surveys of textbooks published from 1880 to 1940. Princeton Professor Edwin Conklin (1921, 34) said in one of his texts that
Comparison of any modern race with the Neanderthal or Heidelberg types shows that... Negroid races more closely resemble the original stock than the white or yellow races. Every consideration should lead those who believe in the superiority of the white race to strive to preserve its purity and to establish and maintain the segregation of the races...
Soon after the American Supreme Court ruled that sterilization of minorities was legal, Adolf Hitler's cabinet, using the American work as an example, passed a eugenic sterilization law in 1933. The German law was compulsory to all people,
...institutionalized or not, who suffered from allegedly hereditary disabilities including feeblemindedness, schizophrenia, epilepsy, blindness, severe drug or alcohol addiction and physical deformities that seriously interfered with locomotion or were grossly offensive (Kevles 1985, 116).
Ironically, the German laws were used to inspire even harsher laws back in the States--in Virginia, Dr. Joseph DeJarnette argued that Americans who were progressive and scientific minded should be shamed by the "enlightened" progressive German legislation, and that we should be taking the lead in this area instead of Germany.
The next step in Germany was for the government to provide "loans" to those couples that it concluded were "racially and biologically desirable" and therefore should have more babies. The birth of each child reduced the "loan" indebtedness by another 25%. Then came sterilization and, in 1939, euthanasia for certain classes of the mentally or physically disabled. Up until this time, many American and British eugenists held up the German program as a model because "it was without nefarious racial content" (Kevles 1985, 188). The German eugenists, on the other hand, repeatedly acknowledged their enormous debt to the American and British researchers and periodically honored eugenists from their universities with various awards.
The Jews in Germany
The German eugenic leadership was originally less anti-semitic than the British. Most German eugenists had originally believed that German Jews were Aryan, and consequently the movement was supported by many Jewish professors and doctors. The Jews were only slowly incorporated into the German eugenic laws which, up to this time, were supported by a large number of persons, both in Germany and abroad.
The Darwinian racists' views also slowly entered into many spheres of German society which they had previously not infected (Beyerchen 1977). The Pan German League, dedicated to "maintaining German Racial Purity" and helping Germans throughout the world resist the tendency to assimilate, was at first not overtly anti-Semitic. Jews who were fully assimilated into German culture were allowed full membership. Many German eugenists would have accepted blacks or gypsies as being racially inferior, but their racial theories did not seem to fit Jews, since they had achieved no small level of success in Germany. Schleunes (1970) adds that by 1903 the influence of racists' ideas permeated the League's program to the degree that its policy changed, and by 1912 the League declared itself based upon "racial principles."
German Jews considered themselves Germans first--and were proud of being such --and Jews second. Their assimilation into German life was to the extent that most were convinced that Germany was now a safe harbor for them.
In spite of the scientific prominence of these racial views, until World War II they had a limited effect upon most Jews. German Jews considered themselves Germans first--and were proud of being such--and Jews second. Many modified the German intelligentsia's racial views by including themselves in it. Their assimilation into German life was to the extent that most were convinced that Germany was now a safe harbor for them (Schleunes 1970, 33). Most felt its anti-Semitic actions did not represent a serious threat to their security. Many still firmly held to the Genesis creation model and rejected the views upon which racism was based, including macro-evolution, and thus, did not see these ideas as a real threat. What happened in Germany later was obviously not well received by Jewish geneticists, even Jewish eugenists, and certain other groups:
The eugenics movement felt a mixture of apprehension and admiration at the progress of eugenics in Germany... [but] the actual details of the eugenics measures which emerged after Hitler's rise to power were not unequivocally welcomed. Eugenicists pointed to the USA as a place where strict laws controlled marriage but where a strong tradition of political freedom existed (Jones 1980, 168).
While in much American and British eugenic literature the Jewish race was still held up as an example of educational and professional achievement, the Germans soon began placing them near the bottom of the list. Further, many American and British eugenists were appalled that the Germans included "many foreign races" as inferior--including many groups such as the Southern and Eastern Europeans, which were respected groups in Britain and America.
Evolution and War in Nazi Germany
Darwinism not only offered the German nation a meaningful interpretation of their recent past, but also a justification for future aggression:
German military success in the Bismarkian wars fit neatly into Darwin categories in the struggle for survival, the fitness of Germany had been clearly demonstrated. [W]as not this expressive of a superior spirit or volksgeist? (Schleunes 1970, 31).
Hitler not only unabashedly intended to produce a superior race, but he openly relied heavily upon Darwinian thought in both his extermination and war policies (Jackel 1972). Nazi Germany thus openly glorified war for the reason that it was an important means of eliminating the less fit of the highest race, a step necessary to "upgrade the race." Clark (1953, 115-116) concludes, quoting extensively from Mein Kampf, that
Hitler's attitude to the League of Nations and to peace and war were based upon the same principles. "A world court... would be a joke... the whole world of Nature is a mighty struggle between strength and weakness--an eternal victory of the strong over the weak. There would be nothing but decay in the whole of nature if this were not so. States which [violate]... this elementary law would fall into decay.... He who would live must fight. He who does not wish to fight in this world where permanent struggle is the law of life, has not the right to exist." To think otherwise is to "insult" nature. "Distress, misery and disease are her rejoinders."
War therefore was a positive force, not only because it eliminated the weaker races, but also because it weeded out the weaker members of the superior races. German greatness, Hitler stressed, came about primarily because they were jingoists, and thereby had been eliminating their weaker members for centuries (Rich 1973). Although Germans were no strangers to war, this new justification was powerful. The view that the process of eradication of the weaker races was a major source of evolution was well expressed by Wiggam (1922, 102):
At one time man had scarcely more brains than his anthropoid cousins, the apes. But, by kicking, biting, fighting... and outwitting his enemies and by the fact that the ones who had not sense and strength... to do this were killed off, man's brain became enormous and he waxed both in wisdom and agility if not in size...
In the long run, war is thus positive, for only by "... kicking, fighting, biting," etc., can humans evolve.
In the long run war is thus positive, for only by "... kicking, fighting, biting," etc., can humans evolve. Hitler even claimed as truth the contradiction that human civilization as we know it would not exist if it were not for constant war. And many of the leading scientists of the day openly advocated this view:
Haeckel was especially fond of praising the ancient Spartans, whom he saw as a successful and superior people as a consequence of their socially approved biological selection. By killing all but the "perfectly healthy and strong children" the Spartans were "continually in excellent strength and vigor" (1876, 170). Germany should follow this Spartan custom, as infanticide of the deformed and sickly was "a practice of advantage to both the infants destroyed and to the community." It was, after all, only "traditional dogma" and hardly scientific truth that all lives were of equal worth or should be preserved (1905, 116) (Stein 1988, 56).
The commonly believed assumption that European civilization evolved far more than others primarily because of its constant warmongering is not true. Historically, many tribes in Africa were continually involved in wars, as were most countries in Asia and America. War is actually typical of virtually all peoples except certain small island groups who have abundant food, or peoples in very cold areas (Posner and Ware 1986).
Nazi policies, therefore, resulted less from a "hatred" toward Jewish or other peoples, than the idealistic goal of preventing "pollution of the race." Hitler (1953, 115-116) elaborated as follows:
Whose fault is it when a cat devours a mouse?... the Jews... cause people to decay... In the long run nature eliminates the noxious elements. One may be repelled by this law of nature which demands that all living things should mutually devour one another. The fly is snapped up by a dragon-fly, which itself is swallowed by the bird, which itself falls victim to a larger bird... to know the laws of nature... enables us to obey them.
We thus must understand and apply the "laws of Nature," such as the survival of the fittest law, which originally produced the human races and is the source of their improvement. We as a race, therefore, must aid in the elimination, or at least the quarantine, of the less fit. In Hitler's words, (1953, 116):
If I can accept a living Commandment, it is this one: "Thou shall preserve the species." The life of the individual must not be set at too high a price. If the individual were important in the eyes of nature, nature would take care to preserve him. Among the millions of eggs a fly lays, very few are hatched out--and yet the race of flies thrives.
Individuals are not only far less important than the race, but the Nazis concluded that certain races, as Whitehead (1983, 115) notes, were not humans, but animals:
The Jews, labeled subhumans, became nonbeings. It was both legal and right to exterminate them in the collectivist and evolutionist viewpoint. They were not considered... persons in the sight of the German government.
Once the inferior races were exterminated, Hitler believed that future generations would thank him profusely for the improvement that his work brought to the world.
Hitler was especially determined to prevent Aryans from breeding with any and all non-Aryans, a concern eventually resulting in the "final solution." Once the inferior races were exterminated, Hitler believed that future generations would thank him profusely for the improvement that his work brought to the world:
The Germans were the higher race, destined for a glorious evolutionary future. For this reason it was essential that the Jews should be segregated, otherwise mixed marriages would take place. Were this to happen, all nature's efforts "to establish an evolutionary higher stage of being may thus be rendered futile" (
Thus, the Darwinist movement was "one of the most powerful forces in the nineteenth-twentieth centuries' German intellectual history [, and] may be fully understood as a prelude to the doctrine of national socialism [Nazism]" (Gasman 1971, xiv). Why did the concepts of evolution catch hold in Germany faster, and take a firmer hold there than any other place in the world?
Evolution Used to Justify Existing German Racism
Schleunes (1970, 30-32), in his discussion of the Nazi policy towards the Jews, noted rather poignantly that the reason the publication of Darwin's 1859 work had an immediate impact in Germany was because
Darwin's notion of struggle for survival was quickly appropriated by the racists... such struggle, legitimized by the latest scientific views, justified the racists' conception of superior and inferior peoples... and validated the struggle between them.
The Darwinian revolution gave the racists what they thought was powerful verification that their race suspicions were "correct." The works of its chief German spokesman and most eminent scientist Haeckel especially provided support (Poliakov, 1974). The support of the science establishment was such that Schleunes (1970, 30-52) notes:
The racists' appropriation of these scientific categories won for racist thought a much wider circulation than its ideas warranted. What satisfaction there must have been to find that one's prejudices were actually expressions of scientific truth...
And what greater authority than science could the racists have for their views? Konrad Lorenz, one of the most eminent animal behavior scientists, often credited with being the founder of the field, stated:
Just as in cancer the best treatment is to eradicate the parasitic growth as quickly as possible, the eugenic defense against the disgenic social effects of afflicted subpopulations is of necessity limited to equally drastic measures... When these inferior elements are not effectively eliminated from a [healthy] population, then--just as when the cells of a malignant tumor are allowed to proliferate throughout the human body--they destroy the host body as well as themselves (Chase 1980, 349).
Lorenz's works were important in developing the Nazi program which was designed to eradicate the parasitic growth. The government's programs about the ways that "German Volk" (people) can maintain their superiority made racism almost unassailable. Although King (1981, 156) claimed that "the holocaust of Nazi persecution... pretended to have a scientific genetic basis," in the minds of those in the government and the universities of the time, its scientific basis was so strong that few contemporary scientists seriously questioned it. The attitudes of the German people were only partly to blame in causing the holocaust--only when Darwinism was added to the preexisting attitudes did a lethal combination result.
Most of the early eugenists, especially in America and Britain, stressed that it was best to rely upon volunteerism to implement their programs. Galton, though, concluded that the situation in his day "was so clear cut and so dire, as to warrant state intervention of a coercive nature in human reproduction" (Kevles 1985, 91). Later, more and more eugenists supported direct government action in applying eugenics laws--if natural selection yielded the Darwinian fit, only artificial selection enforced by the government could insure that only the eugenically superior multiplied. Many social workers and psychiatrists in Britain, the United States, and Germany were convinced of the heredity origin of social deficiencies, and, in more and more countries, they felt compelled to force the government to intervene. In no country was this intervention as successful as in Germany. Discouraged by the lack of effectiveness of their science, and fully convinced that it had adequately been empirically supported with the brilliant work of Charles Darwin, Karl Pearson, Francis Galton and many others, Western scientists felt envy that only Germany was able to implement the programs which many scientists of America and Europe were then strongly advocating (Chase 1980).
...in the minds of those in the government and the universities of the time, its scientific basis was so strong that few contemporary scientists seriously questioned it.
Nazi Germany was certainly not alone in applying science to government. As Kevles (1985, 101) states, "In the United States during the opening decades of the century, it came to be a hallmark of good reform to shape government with the aid of scientific experts... eugenics experts aplenty were to be found in the biology, psychology, and sociology departments of universities or colleges... " And the German eugenics programs elicited in little opposition from the United States. The implications of its eugenic immigration acts, especially the American Johannson act quotas of 1924, a law not repealed in 1941, had enormous consequences for human lives.
At least nine-million human beings of what Galton and Pearson called degenerative stock, two-thirds of them the Jews... continued to be denied sanctuary at our gates. They were all ultimately heralded into Nordic Rassenhygiene camps, where the race biologist in charge made certain that they ceased to multiply and ceased to be (Chase 1980, 360).
The first step was to determine which groups were genetically superior, a judgment that was heavily influenced by one's culture. Many Germans believed that the American and British choices for the inferior races were incorrect; thus, they instituted their own program to determine who were the superior races. This meant that they must first determine which are superior, and then specifically what traits would place a person in a superior and/or in an inferior race.
The first step was to determine which groups were genetically superior, a judgment that was heavily influenced by one's culture.
In trying to group persons into races to select the "best" Germans to serve as "official" child breeders, the Nazis measured a wide variety of physical traits, such as brain case sizes. Although superficial observations enable most people to make a rough classification based on white, black and oriental, when the race question is explored in depth, such divisions are by no means easy, as the Nazis soon found out. It was further made difficult in that, with many of the groups that they felt inferior, such as the Slovaks, Jews, Gypsies, and other groups, it was not easy to distinguish them from the pure "Aryan" race. In general, the Nazis relied heavily upon the work of Hans F.K. Gunther, who was a professor of racial science at the University of Gena. As Mosse (1981:57) acknowledged, although Gunther's "personal relationships with the party were stormy at times, his racial ideas were accepted" and received wide support throughout German government and were an important influence in German policy. Gunther recognized that, while "a race may not be pure, its members share certain dominant characteristics, thus paving the way for stereotyping (Mosse 1981:57). The goal was to find the racial "ideal type."
Gunther concluded that all Aryans share an ideal Nordic type which contrasted with the Jews, who, he concluded, were a mixture of races.
He concluded that all Aryans share an ideal Nordic type which contrasted with the Jews, who, he concluded, were a mixture of races. Gunther stressed both anthropological measurement of skulls, as well as an evaluation of a person's physical appearance. The predominance of such characteristics and a person's genealogical lineage were used as criteria. Even though physical appearance was stressed, the key was that "the body is the showplace of the soul" and "the soul is primary" (Mosse 1981:58). Select females were placed in special homes and kept pregnant as long as they were in the program. Even though the researchers tried to choose persons with the ideal traits, the I.Q.'s of the resulting offspring were generally lower than that of the parents. Research on the offspring of this experiment has concluded, as is now known, that I.Q. regresses toward the population mean.
The evolutionary views not only influenced the Nazi attitude toward Jews, but other cultural and ethnic groups as well. Even mental patients were massacred, in part because it was believed at the time that heredity had a major influence on mental illness. Mental patients were not the products of a sick environment, but a sick gene line (or perhaps they had some Jewish or other non-Aryan blood in them). Consequently, they had to be destroyed. Poliakov (1974, 282) notes that many intellectuals in the early 1900s accepted telegony, the idea that bad blood would contaminate a race line forever, or that "bad blood drives out good, just as bad money displaces good money." Only extermination would permanently eliminate "weak" and inferior genetic lines and, thereby, further evolution.
Numerous respected biologists supported this position--Darwin even compiled a long list of cases where "bad blood" polluted a whole gene line, causing it to bear impure progeny forever. Ernst Ruedin, of the University of Munich, and many of his colleagues (such as Herbert Spencer, Francis Galton, Calaude Bermand and Eugene Kahn, later a professor of psychiatry at Yale) actively advocated this "hereditary argument." They were also the chief architects of the compulsory German sterilization laws which were designed to prevent those with defective or "inferior" genes from "contaminating" the Aryan gene pool. Later, when the "genetically inferior" were also judged to be "useless dredges," massive killings became justified. The groups judged "inferior" were gradually expanded to include a wide variety of races and national groups. Later, they even included less healthy older people, epileptics, mental defectives (both severe and mild), deaf-mutes, and those with terminal illnesses (Wertham 1966, Chase 1980).
Mengele's zeal (at Auschwitz) was based on highly accepted mainline science theory, not on alleged sadistic or psychopathic impulsives.
The justification for this killing, repeated over and over again, was that the "leading biologists and medical professors" advocated the program. Dr. Carl Brandt, according to Wertham (1966, 160), felt that since the learned professors were in support of it, the program must be valid, and "who could there be who was better qualified [to judge it] than they?" The scientist who presided over the race program at Auschwitz, Dr. Josef Mengele, was a highly respected and published researcher who held a Ph.D. from the prestigious University of Munich, and an M.D. from the University of Frankfort (Astor 1985). His zeal was based on highly accepted mainline science theory, not on alleged sadistic or psychopathic impulsives (Posner and Ware, 1986). His biographer (Astor 1985, 21) concluded that
Race purity and the contaminant threat of Jews became gospel in lower and higher education. When Mengele began his college studies at the University of Munich, anti-Semitism had already sprouted in the sciences .... The impressionable young man... soaked up writings like those of a German oriental scholar, Parl de Lagarde, who despised "those who out of humanity defend these Jews, or who are too cowardly to trample these usurious vermin to death.... With trichinae and bacilli one does not negotiate, nor are trichinae and bacilli to be educated. They are exterminated as quickly and thoroughly as possible."
And Posner and Ware (1986, 23) add:
In Munich, meanwhile, Joseph was taking courses in anthropology and paleontology as well as medicine... his real interest in genetics and evolution happened to coincide with the developing concept that some human beings afflicted by disorders were unfit to reproduce, even to live... His consummate ambition was to succeed in this fashionable new field of evolutionary research [Italics added].
The groups included as "inferior" were later expanded to include persons who had only Negroid or mongoloid features, gypsies, and those who did not "pass" a set of ingeniously designed overtly racist phrenology tests now known to be worthless (Davies 1955). After Jessie Owen won several gold medals at the 1936 Berlin Olympics, Hitler stated that "the Americans ought to be ashamed of themselves" for even permitting blacks to enter the contests (Stanton 1972). Some even advocated the view that women were evolutionarily inferior to men. Dr. Robert Wartenberg, who later became a prominent neurology professor in California, tried in one monograph to "prove" women's inferiority, stressing that they could not survive unless they were "protected by men," and females evolved "weak" because of historically being protected by males. For this reason, he concluded that natural selection had not been as operative on women to the extent it had been on men. Thus, the weaker women were not eliminated as rapidly, resulting in a slower rate of evolution. How the weak were to be "selected" for elimination was not clear, nor were the criteria used to determine "weak." Women in Nazi Germany were openly prohibited from entering certain professions and were required by law to conform to a traditional female role (Weindling 1989).
After Jessie Owen won several gold medals at the 1936 Berlin Olympics, Hitler stated that "the Americans ought to be ashamed of themselves"for even permitting blacks to enter the contests.
Current writers often gloss over, totally ignore, or even distort the close connection between Darwinian evolution and the Nazi race theory and the policies that it produced, but, as Stein (1988, 50) admonishes,
There is little doubt that the history of ethnocentrism, racism, nationalism, and xenophobia has also been a history of the use of science and the actions of scientists in support of these ideas and social movements. In many cases it is clear that science was used merely as raw material or evidence by ideologically interested political actors as proof of preconceived notions. Most contemporary sociobiologists and students of biopolitics would argue that all attempts to use science in this manner are, in fact, mere pseudoscience... On the other hand, there is also little doubt in the historical record that this contemporary self-protecting attitude is based on a somewhat willful misreading of history. The history of ethnocentrism and the like has also been the history of many well-respected scientists of the day being quite active in using their own authority as scientists to advance and support racist and xenophobic political and social doctrines in the name of science. Thus, if the scientists of the day used the science of the day to advance racism, it is simply a form of Kuhnian amnesia or historical whitewash to dismiss concern with a possible contemporary abuse of science by a claim that the past abuse was mere pseudoscience.
The literature contains only a few studies which directly deal with this issue--and many avoid it because evolution is inescapably selectionist. The very heart of the theory of evolution is survival of the fittest--and this requires differences among a species which in time will become great enough so that those individuals that possess them--the fittest--are more apt to survive, manifesting differential survival rates. Although the process of raciation may begin with slight differences, evolution in time produces distinct races which results from speciation, or the development of a new species.
Nazism and Religion
Much of the opposition to the eugenic movement came from the German Christians. Although Hitler was once an altar boy and then "considered himself a good Roman Catholic," (Zindler 1985, 29), as an adult, he clearly had strong anti-religious feelings, as did many of the Nazi party leaders. As would any good politician, though, he openly tried to exploit the church's influence (Phillips 1981, 164). His feelings on religion were once bluntly stated:
The organized lie [religion] must be smashed. The State must remain the absolute master. When I was younger, I thought it was necessary to set about [destroying religion] with dynamite. I since then realized there's room for subtlety.... The final state must be, in St. Peter's Chair a senile officiant; facing him a few sinister old women.... The young and healthy are on our side... It's impossible to eternally hold humanity in bondage and lies... [It] was only between the sixth and eighth centuries that Christianity was imposed upon our people... Our people had previously succeeded in living all right without this religion. I have six divisions of SS men absolutely indifferent in matters of religion. It doesn't prevent them from going to their death with serenity in their souls (1953, 17).
"Christianity makes no distinction of race or of color ... In this respect the hand of Christianity is against that of Nature, for are not the races of mankind the evolutionary harvest which Nature has toiled through long ages to produce?"
His beliefs are abundantly clear: the younger people who were the hope of Germany were "absolutely indifferent in the matters of religion." As Keith (1946, 72) noted, the Nazi party viewed evolution and Christianity as polar opposites because
Christianity makes no distinction of race or of color; it seeks to break down all racial barriers. In this respect the hand of Christianity is against that of Nature, for are not the races of mankind the evolutionary harvest which Nature has toiled through long ages to produce? May we not say, then, that Christianity is anti-evolutionary in its aim?
The opposition to religion was a prominent feature of German science, and thus later German political theory, from its very beginning. As Stein (1988, 54) summarized:
Ernst Haeckel... in a lecture entitled "On evolution: Darwin's Theory"... argued that Darwin was correct... humankind had unquestionably evolved from the animal kingdom. Thus, and here the fatal step was taken in Haeckel's first major exposition of Darwinism in Germany, humankind's social and political existence is governed by the laws of evolution, natural selection, and biology, as clearly shown by Darwin. To argue otherwise was backward superstition. And, of course, it was organized religion which did this and thus stood in the way of scientific and social progress.
Borman was equally blunt, stressing that the church's opposition to the forces of evolution must be condemned. In his words:
National Socialist [Nazi] and Christian concepts are incompatible. The Christian Churches build upon the ignorance of men and strive to keep large portions of the people in ignorance... On the other hand, National Socialism is based on scientific foundations. Christianity's immutable principles, which were laid down almost two thousands years ago, have increasingly stiffened into life-alien dogmas. National Socialism, however, if it wants to fulfill its task further, must always guide itself according to the newest data of scientific researches. (Quoted in Mosse 1981, 244.)
Borman also concluded that:
The Christian Churches have long been aware that exact scientific knowledge poses a threat to their existence. Therefore, by means of such pseudo-sciences as theology, they take great pains to suppress or falsify scientific research. Our National Socialist world view stands on a much higher level than the concepts of Christianity, which in their essentials were taken over from Judaism. For this reason, too, we can do without Christianity (Mosse 1981, 244).
From our modern perspective, WW II and its results ensued from the ideology of an evil madman and his administration. Hitler, though, did not see himself as evil, but as mankind's benefactor. He felt that many years hence the world would be extremely grateful to him and his programs, which lifted the human race to genetically higher levels of evolution by preventing mixed marriages with inferior races. His efforts to put members of these inferior races in concentration camps was not so much an effort to punish but, as his apologists repeatedly stated, was a protective safeguard similar to quarantining sick people to prevent contamination of the community. Or, as Hoess (1960, 110) adds, "such a struggle, legitimized by the latest scientific views, justifies the racists' conceptions of superior and inferior people and nations and validated the conflict between them."
Some Conclusions
Although many factors produced the fatal blend which produced the Nazi movement, Darwin's notion of struggle for survival was appropriated to justify the movement's views, not only on race, but also war. One contributing reason, if not a major reason, that matters reached the extent of the holocaust was the acceptance of Social Darwinism by the scientific and academic community (Aycoberry 1981, Beyerchen 1977, Stein 1988). Misuse of Darwin's theory, as modified by Haeckel (1876, 1900, 1903, 1905, 1916), Chamberlain (1911), and others thus contributed to the death of a total of over nine million persons in concentration camps, and approximately forty million other human beings in a war that cost about six trillion dollars. Although it is no easy task to fully assess the conflicting motives of Hitler and his party, eugenics clearly played an important part. If the Nazi party had fully embraced and consistently acted on the belief that all humans are brothers, equal before God, it can be argued that the holocaust probably never would have occurred. Expunging the Judeo-Christian-Moslem doctrine of divine human origins from mainline German theology and its schools openly contributed to the acceptance of Social Darwinian theory, resulting in the tragedy of World War II (Chase 1980).
©1992
REFERENCES
Astor, Gerald. The Last Nazi: The Life and Times of Joseph Mengele. New York: Donald Fine Co., 1985.
Aycoberry, P. The Nazi Question: An Essay on the Interpretations of National Socialism. 1922-1975, New York: Pantheon, 1981.
Barzum, Jacques. Darwin, Marx, Wagner. Garden City, NY: Doubleday Anchor Books, 1958.
Bergman, Jerry. "A Short History of Wars and Holocausts." Paper submitted for publication, 1988.
Beyerchen, A.D. Scientists Under Hitler. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1977.
Chamberlain, Houston. The Foundations of the Nineteenth Century. 2 Vols. London: Lane, 1911 (First ed. 1899).
Chase, Allan. The Legacy of Malthus: The Social Costs of the New Scientific Racism. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1980.
Clark, Robert. Darwin: Before and After. Chicago, IL: Moody Press, 1953.
Cohn, N. Warrant for Genocide. New York: Scholow Press, 1981.
Conklin, Edwin G. The Direction of Human Evolution. New York: Scribners, 1921.
Davies, John D. Phrenology: Fad and Science. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1955.
Farrar, Straus and Young. Hitler's Secret Conversations: 1941-1944. With an introductory essay on The Mind of Adolf Hitler by H.R. Trevor-Roper. New York: Farrar, Straus and Young, 1953.
Gasman, Daniel. The Scientific Origin of National Socialism. New York: American Elsevier, 1971.
Gould, Stephen Jay. Ontogeny and Phylogeny. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1977.
Haeckel, E. The History of Creation: Or the Development of the Earth and Its Inhabitants by the Action of Natural Causes. New York: Appleton, 1876.
_________. The Riddle of the Universe. New York: Harper, 1900.
_________. The Evolution of Man. New York: Appleton, 1903.
_________. The Wonders of Life. New York: Harper, 1905.
_________. Eternity: World War Thoughts on Life and Death, Religion, and the Theory of Evolution. New York: Truth Seeker, 1916.
Haller, John S., Jr. Outcasts From Evolution: Scientific Attitudes to Racial Inferiority, 1859-1900. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 1971.
Hickman, Richard. Biocreation. Worthington, OH: Science Press, 1983.
Hitler, Adolf. Hitler's Secret Conversations. New York: Farrar, Straus and Young, 1953.
Hoess, Rudolf. Commandant of Auschwitz. Cleveland: World Publishing Co., 1960.
Hooton, Earnest Albert. Why Men Behave Like Apes and Vice Versa or Body and Behavior. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1941.
Humber, Paul. "The Ascent of Racism." Impact, Feb. 1987, pp. 1-4.
Jackel, E. Hitler's Weltanschauung. Middletown, CT: Wesleyan University Press, 1972.
Jacquard, Albert. In Praise of Difference: Genetics and Human Affairs. New York: Columbia University Press, 1984.
Jones, Greta. Social Darwinism and English Thought: The Interaction Between Biological and Social Theory. Atlantic Highlands, NJ: The Humanities Press, 1980.
Keith, Arthur. Evolution and Ethics. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1946.
Kevles, Daniel J. In the Name of Eugenics: Genetics and the Uses of Human Heredity. New York: Alfred A. Knopf Company, 1985.
King, James. The Biology of Race. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 2nd, Ed., 1981.
Lappe, Marc. "Eugenics," In The Encyclopedia of Bioethics. New York: The Free Press, 1978.
Mosse, George L. Nazi Culture: Intellectual, Cultural, and Social Life in the Third Reich. New York: Schocken Books, 1981.
Phillips, Kevin. Post-Conservative America: People, Politics, and Ideology in a Time of Crisis. New York: Random House, 1981.
Poliakov, Leon. The Aryan Myth. (Translated by Edmund Howard) New York: Basic Books, 1974.
Posner, G.L. and J. Ware. Mengele. New York, McGraw Hill Book Company, 1986.
Proctor, Robert N. Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1988.
Rauschning, Hermann. The Revolution of Nihilism. New York: Alliance Book Corp., 1939.
Rich, N. Hitler's War Aims. New York: Norton, 1973.
Rudorff, Raymond. Studies in Ferocity. New York: The Citadel Press, 1969.
Schleunes, Karl A. The Twisted Road to Auschwitz. Urbana IL: University of Illinois Press, 1970.
Stanton, William. The Leopard's Spots: Scientific Attitudes Towards Race in America, 1815-1859. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 1972.
Stein, George "Biological Science and the Roots of Nazism." American Scientist, Vol. 76, No. 1, Jan-Feb., 1988, pp. 50-58.
Tenenbaum, Joseph. Race and Reich. New York: Twayne Pub., 1956.
The Nuremberg Trials. Vol. 14, Washington DC: GPO, 1946.
Tobach, Ethel and John Gianusos, Howard R. Topoff, and Charles G. Gross. The Four Horsemen: Racism, Sexism, Militarism, and Social Darwinism. New York: Behavioral Publications, 1974.
Weindling, Paul. Health, Race and German Politics Between National Unification and Nazism 1870-1945. Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press, 1989.
Weiss, Sheila Faith. Race Hygiene and National Efficiency: The Eugenics of Wilhelm Schallmayer. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1988.
Wertham, Frederic. A Sign for Cain. New York: The Macmillan Co., 1966.
Whitehead, John. The Stealing of America. Westchester, IL: Crossway Books, 1983.
Wiggan, Albert Edward. The New Dialogue of Science. Garden City, NY: Garden City Publishing Co., 1922.
Wilder-Smith, Beate. The Day Nazi Germany Died. San Diego, CA: Master Books, 1982.
Zindler, Frank R. "An Acorn Is Not an Oak Tree." American Atheist. August, 1985.